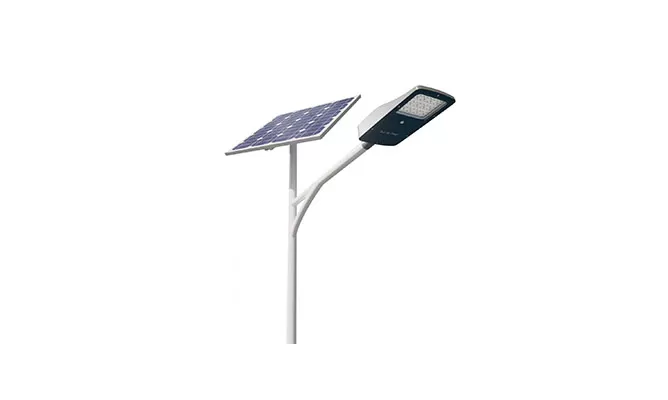
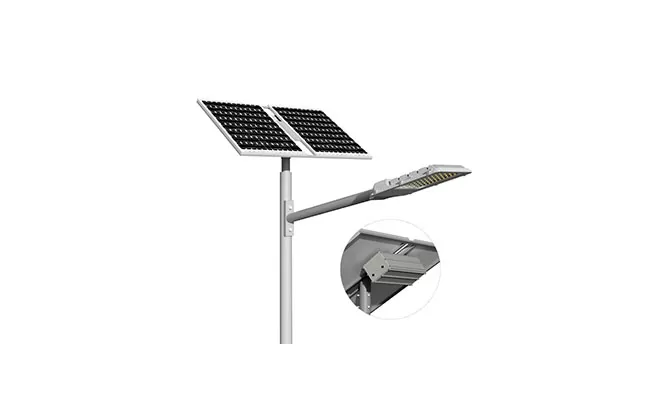
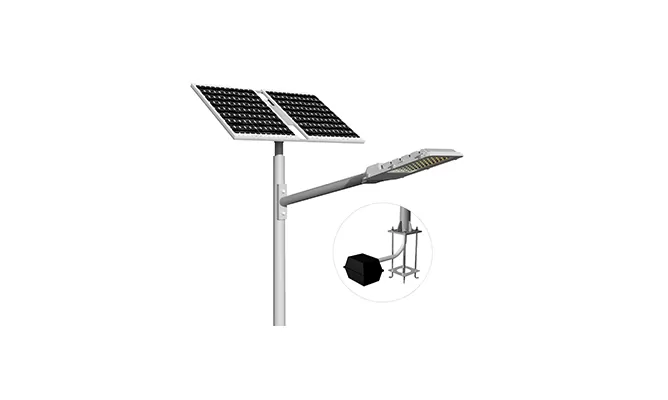
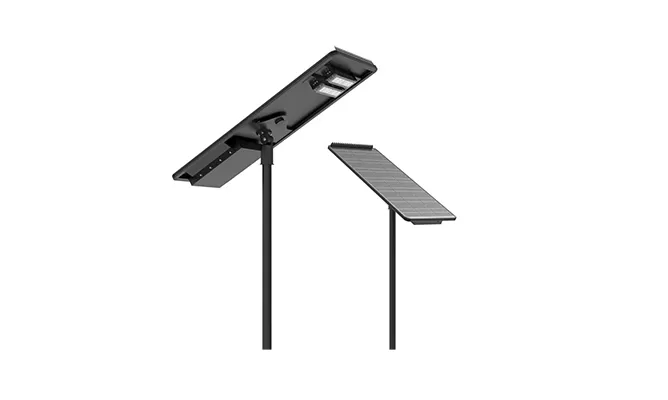
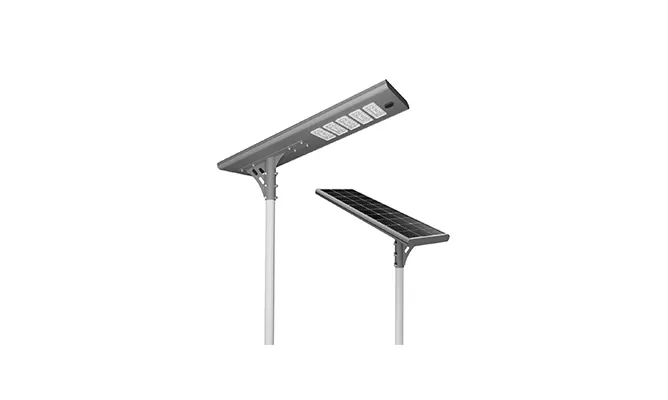
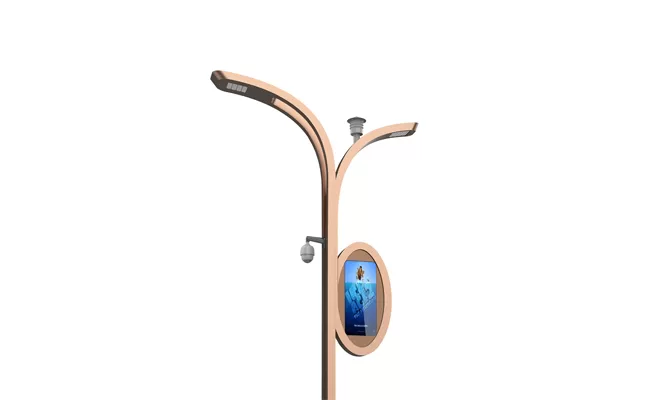
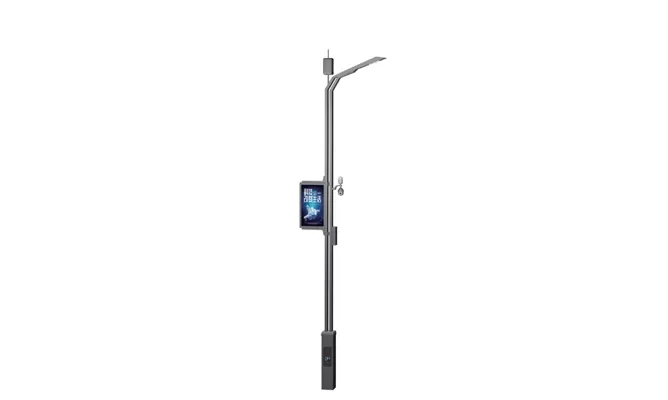
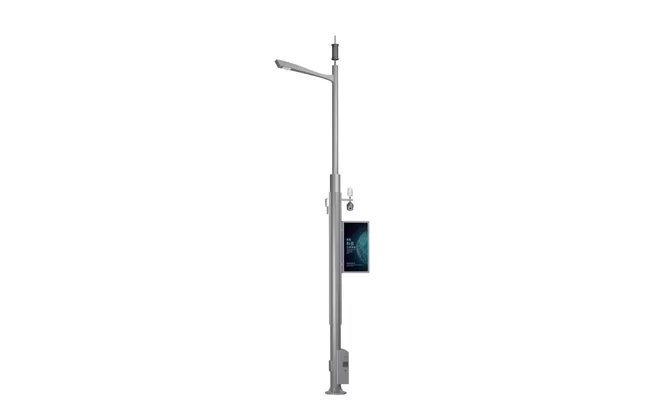
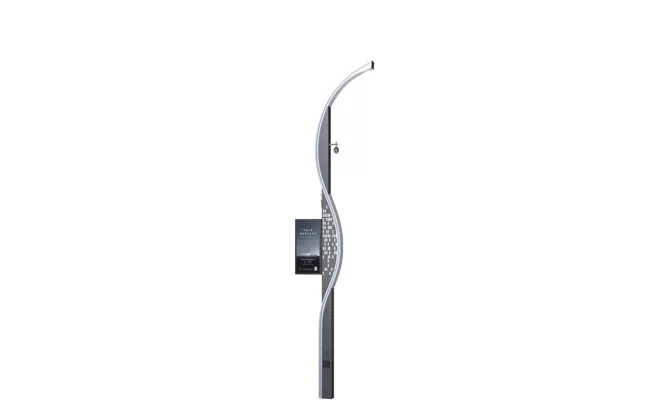
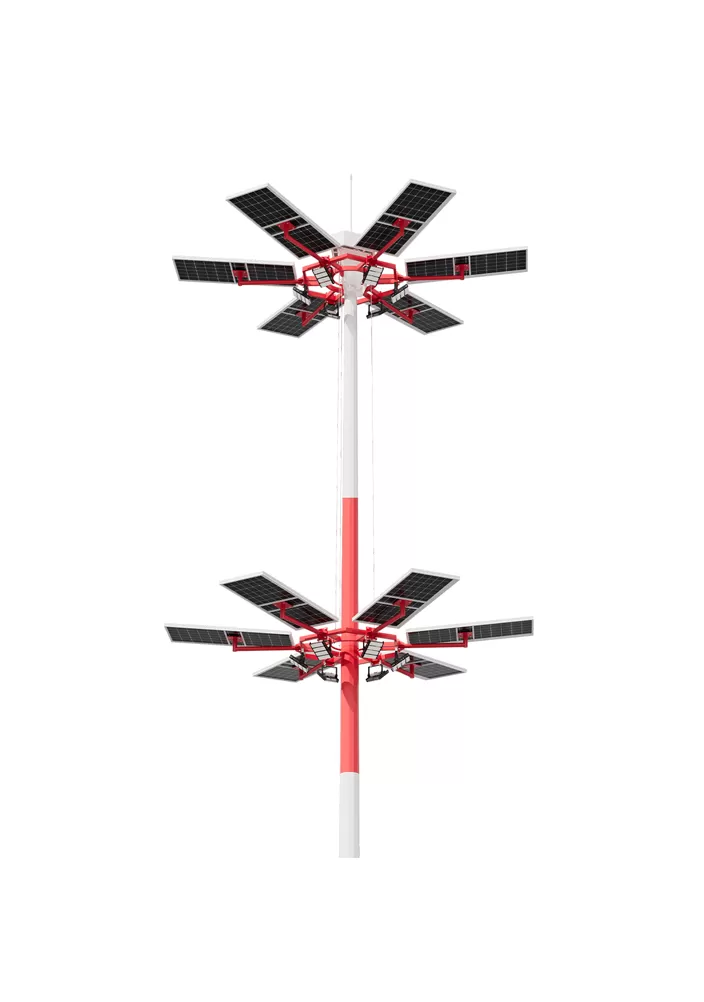
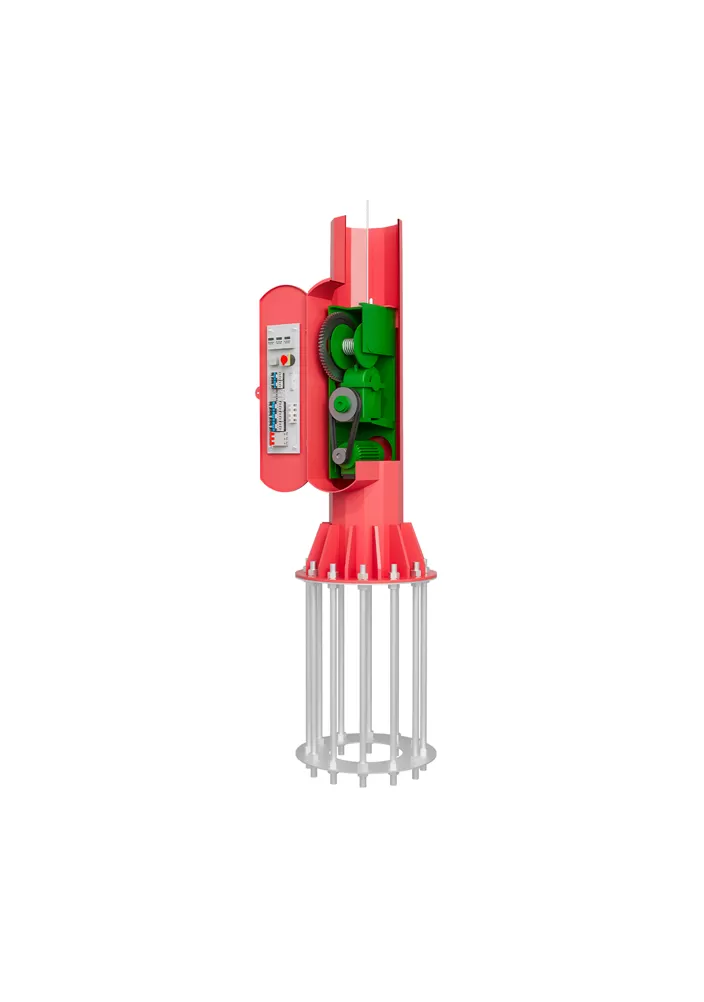
- > Split Solar Street Light
- > All in One Solar Street Light
- > Solar Pole Light
- > Smart Solar Street Light
- All in Two Solar Street Light
- Solar Street Light with Lithium Battery
- Solar Street Light with Gel Battery
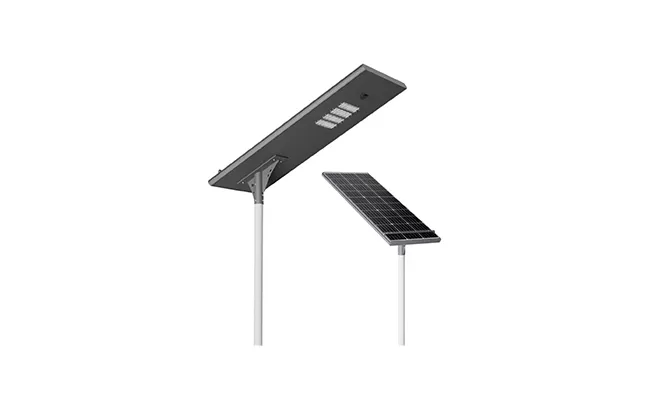
- New All in One Solar Street Light
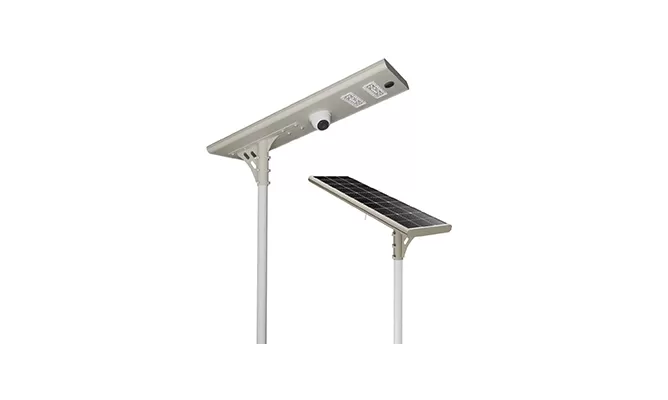
- All in One Solar Street Light with CCTV
- Auto Clean All in One Solar Street Light
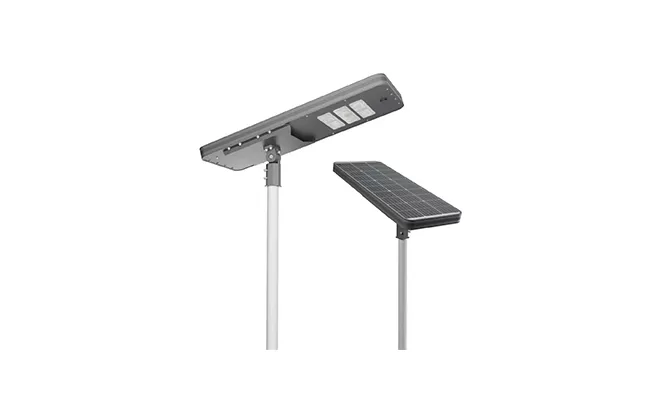
- Intelligent Control All in One Solar Street Light
Cases
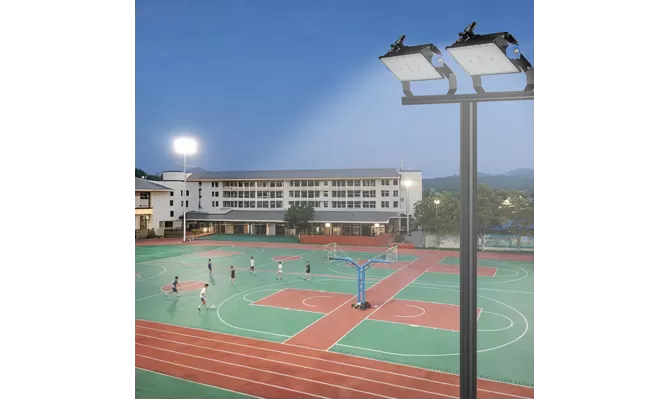
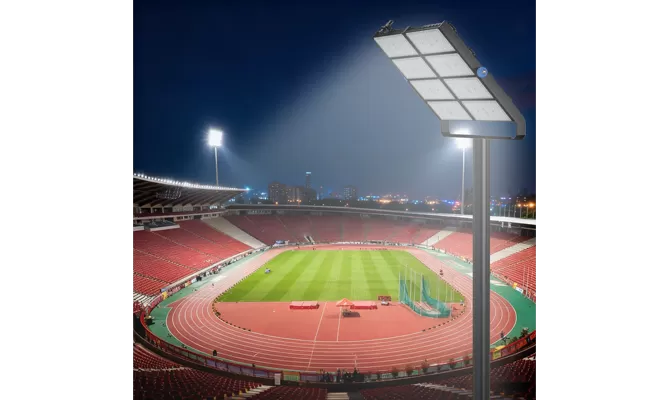
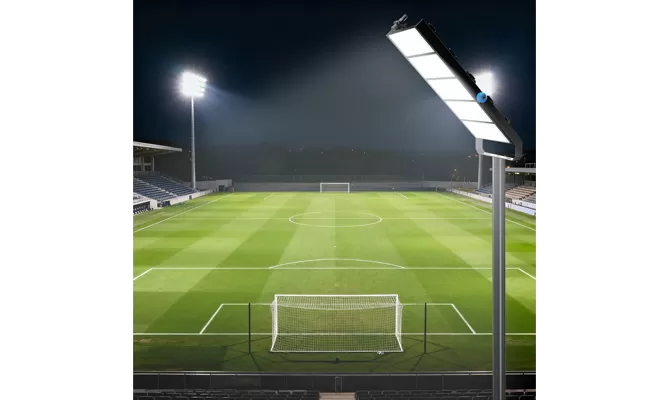
- Stadium Lights
- All in One Solar Street Lights
- Decorative Light Poles
- Split Solar Street Lights
- Guizhou Province Rural Revitalization Comprehensive Lighting Project | Solar Street Light OEM Cooperation Case
- Abuja Airport Peripheral Road Project | International OEM Case of Smart Solar Street Lights
- Long-Term Brand Partnership Case | Strategic ODM / OEM Cooperation in Smart Photovoltaic Lighting
En
What are you looking for?